IJPEM-ST
AI-assisted Monitoring of Human-centered Assembly: A Comprehensive Review
A Comprehensive Review on Concurrent Smart Technology on Human-centered Assembly Process
민상기/University of Wisconsin-Madison
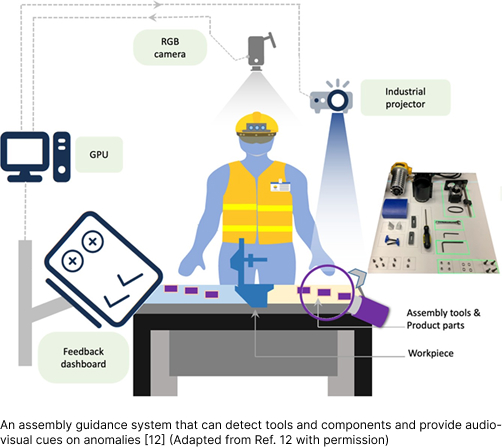
- Smart manufacturing pursues various objectives including full automation to boost productivity and remove uncertainty, flexible manufacturing to corresponding to high mix/high volume or high mix/low volume manufacturing, and further full integration of entire manufacturing ecosystem. The biggest challenge in full automation is assembly process where a human is involved in. Autonomous assembly operations monitoring is not trivial due to the varying length of fine-grained SOP steps and anthropometric variations associated with assembly workers. Hence, various approaches have been made, but again human’s anthropometric aspect failed or prevent effective implementation of such approaches. Among many technical challenges, this paper focuses on monitoring of human actions with the following highlights.
• Monitoring methodologies: the existing methodologies, and approaches to detect and localize actions will be reviewed. The domain of application for action detection and localization will include manufacturing assembly operations but may not be limited to it. Additionally, in this section, we aim to draw a contrast between the current state of the art for action localization and their prospective applications towards manufacturing assembly operations.
• Anomalies in assembly monitoring: An overview of what constitutes an anomaly in human-centric assembly operation is discussed.
• Evaluation metrics: an overview of several metrics used to evaluate the models for assembly action detection and localization is presented. The evaluation metrics are classified into Generic and Specific. Generic evaluations are common and are used external to action localization, whereas the specific evaluations are more catered to action localization studies and assembly monitoring.
 메뉴열기
메뉴열기
